HØST PtX Esbjerg is a green ammonia plant under development, deploying industrial use of electrolysis-technology on GW-level. The plant will rely on electricity from renewables as the sole source of energy. The outcome of this CO2-free production process is green hydrogen and ultimately the end-product green ammonia.
The ammonia plant is relying on proven electrolysis technology, which is considered fully mature and ready for commercial scale deployment. HØST PtX Esbjerg will furthermore deploy the conventional Haber-Bosch process. Haber-Bosch is the main industrial procedure for the production of ammonia today, in which nitrogen reacts with hydrogen under high temperature and pressure using a catalyst to produce ammonia.
By producing green ammonia, HØST PtX Esbjerg will open the door to decarbonization of hard-to-abate sectors such as shipping, agriculture and industrial applications. Five Danish industry leaders have committed themselves to offtake green ammonia from the plant. DLG, Danish Crown and Arla represent the dairy and agricultural industry, while DFDS and Maersk are the leading shipping and logistics companies in the group.
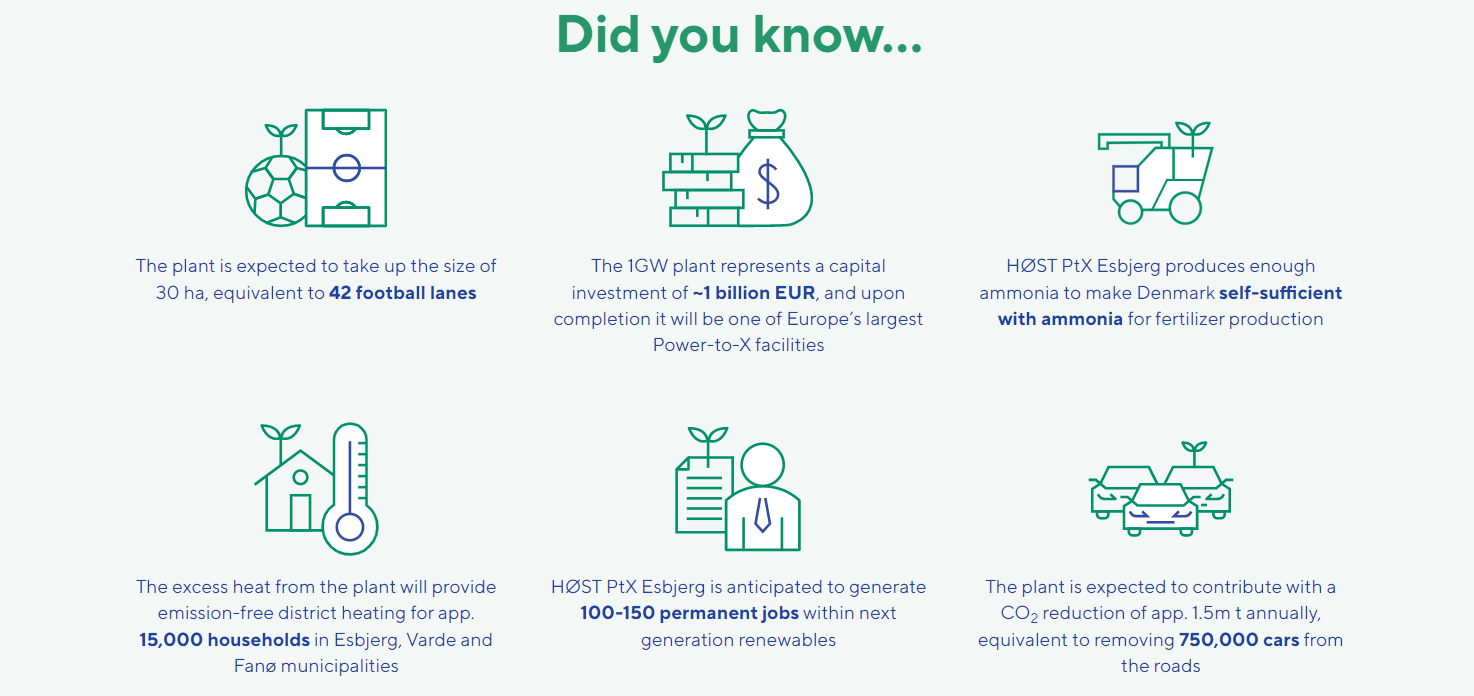
But the benefits of the facility don’t stop there. The flexible operation of HØST PtX Esbjerg will ensure efficient use of the electricity being fed into the Danish energy system from the planned 10GW offshore wind build-out in the North Sea. Furthermore, the process heat from the production of hydrogen and ammonia will be utilized for district heating of 15,000 households in the Esbjerg/Varde area by the local utility company, DIN Forsyning. Additionally, because the PtX process requires large volumes of water DIN Forsyning is now investigating whether treated wastewater can be used in the process, instead of using groundwater, adding to the sustainable potential of the project.
With a capital investment of more than 1 billion EUR, HØST PtX Esbjerg will be the leading PtX plant in Denmark. The project will also be among the first gigawatt-scale PtX facilities in Europe, contributing to the much-needed acceleration of the decarbonization journey towards carbon neutrality in 2050. HØST PtX Esbjerg will make a 1GW contribution to EU’s target of 40GW of electricity coming from renewable hydrogen electrolysers by 2030.
The development of the project is expected to be made in 2-3 years, followed by final investment decision in early 2023. Construction of the project is expected to be finalized in 2026. HØST is a project company under the management of Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP). CIP specialises in energy infrastructure investments and is among the largest fund managers globally within renewables.