About the white paper
State of Green is launching a new white paper on sector coupling highlighting Danish experiences with building an integrated energy system.
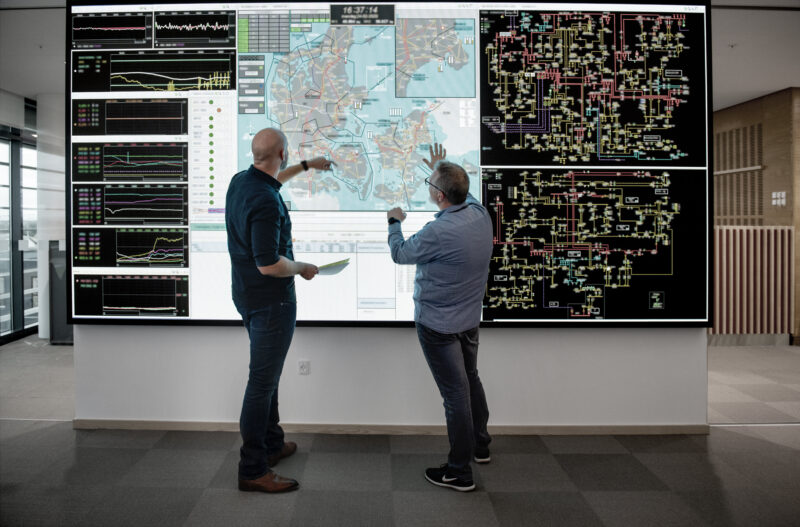
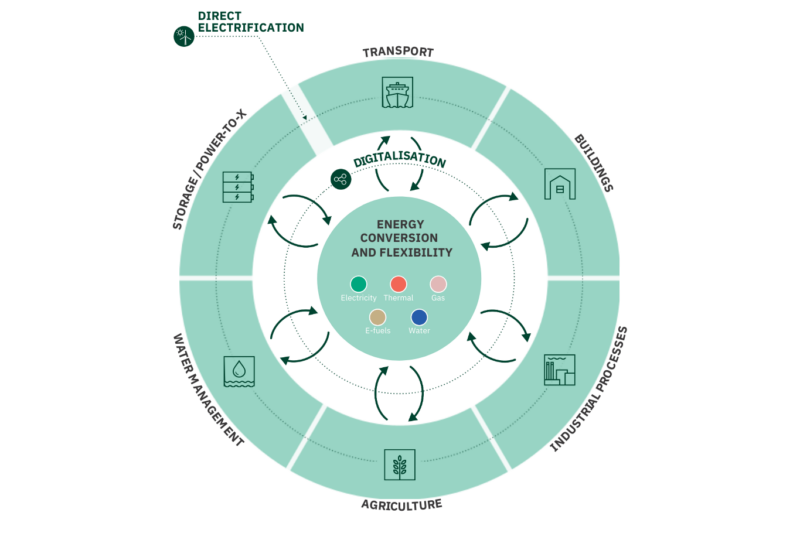
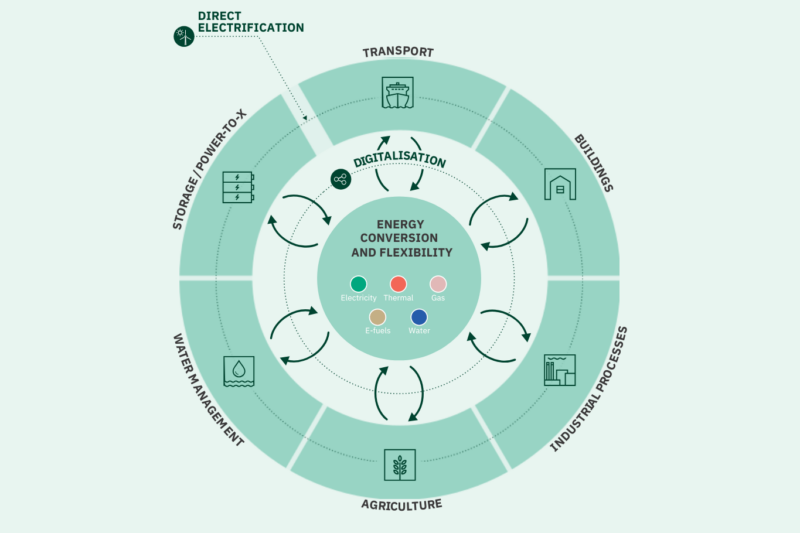
Sector coupling is an innovative approach that involves the integration of various energy sectors to maximise the utilisation of renewable energy in the most energy-efficient way. In many ways, it heralds a paradigm shift in how we approach energy management and decarbonisation. It involves dismantling traditional silos between different forms of energy, fostering partnerships and collaboration across sectors and industries, both locally, nationally and internationally.
This white paper presents highlights on sector coupling in a Danish context with a focus on energy. Showcasing more than 20 cases on sector coupling from Danish solutions providers, it presents an overview of how Denmark works to utilise renewable energy in sectors such as heating, cooling, transport, production industries and farming, while at the same time securing a high degree of energy efficiency and security of supply.
The white paper is developed in close collaboration with Danish Energy Agency, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark, Danish Industry, Green Power Denmark, Danish Agriculture & Food Council and the public-private foundation GESEK – Green Energy and Sector Coupling.
Discover the publication