Technology and innovation are building blocks for a global green transition. Denmark can become an ideal living lab for CCUS, fostering innovation and testing new technologies.
Attracting foreign talents and global companies is needed to gather the skills and fill the gaps in the existing workforce, which will ultimately be beneficial to the economy. It is essential to ensure Danish companies’, researchers’ and institutions’ continued and improved competitiveness, and to help secure Denmark’s position as a leading knowledge society.
Taking leadership on innovative solutions means a strong collaboration between businesses and universities, as well as developing a talent-pool of highly qualified labour. Denmark offers flexible business conditions and an internationally-oriented workforce. By building a nationwide CCUS ecosystem, Denmark can become a key location for CO₂ storage and utilisation.
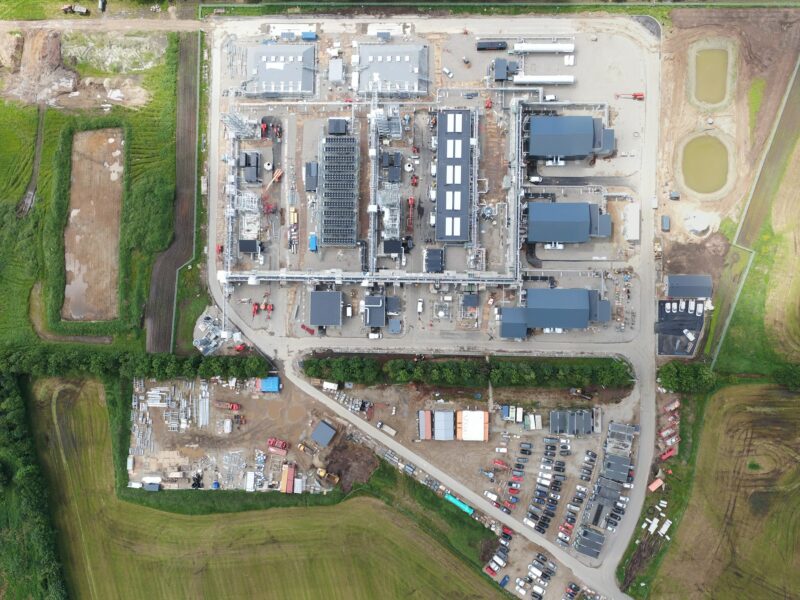
Testing and scaling up
The Danish commitment to the clean energy transition means a stable and predictable framework for long-term investments. It also means access to a variety of actors across the full supply chain in related sectors like renewable energy production, green hydrogen, Power-to-X and sustainable fuels for trucks, shipping and aviation.
Denmark’s advanced position on biomass-fired combined heat and power plants, biogas, solid waste incineration and cement production means companies have good local opportunities for testing and commercialising carbon capturing solutions on these carbon sources and creating the foundation for subsequent technology exports to other countries.
Moving from being CCUS entrepreneurs of innovation to growing business opportunities requires identification of investment potentials and public-private commitment to scale up solutions.
New solutions to be commercialised
The use of carbon capture depends on several factors including technology development, commercial viability, alternative fuel prices and availability, and future emission-related regulatory requirements. Further analyses and developments are required to maximise emission reduction and minimise costs, as well as developing business models that would allow utilisation and/or storage of the carbon capture.
Although the emissions reduction potential of CCUS is significant, its CO₂ abatement costs are currently high. The incentive structures need to be in place working efficiently to demonstrate market-based success.