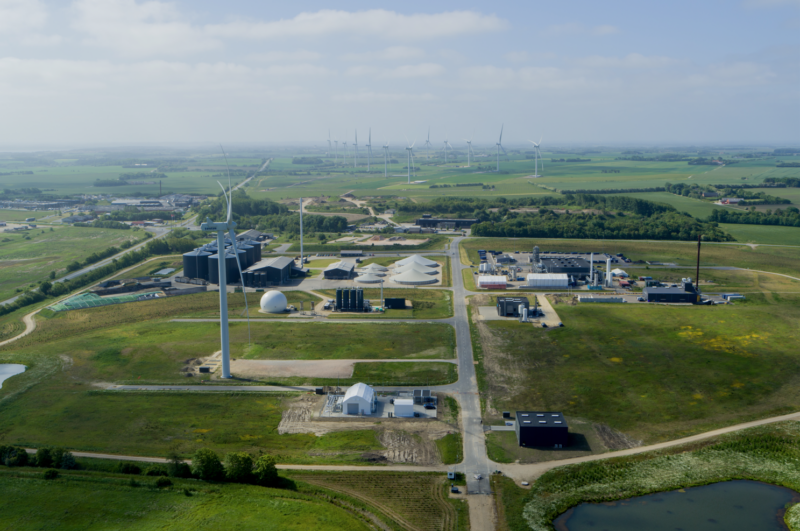
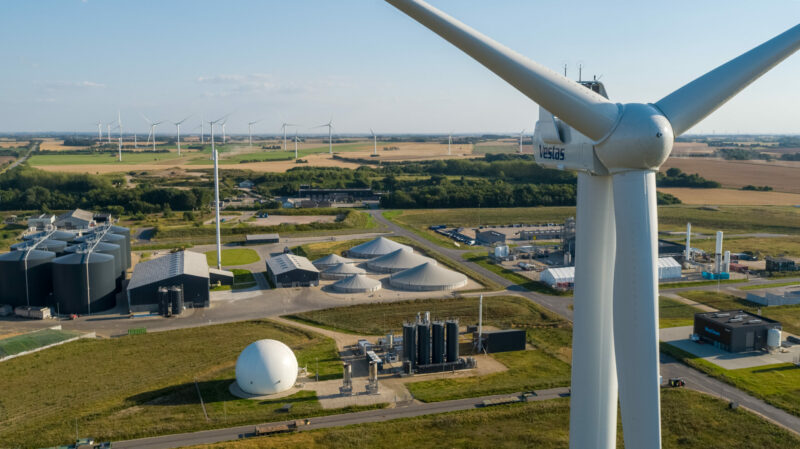
With decades of global focus on addressing the climate crisis, the main challenge has become evident: Replace all fossil energy sources with renewable energy. In Denmark, this transition is well underway, and Denmark is renowned for its high share of renewable energy, especially wind, in its energy mix. In 2023, almost 44 percent of Denmark’s actual energy consumption was covered by renewable energy (source: Danish Energy Agency).
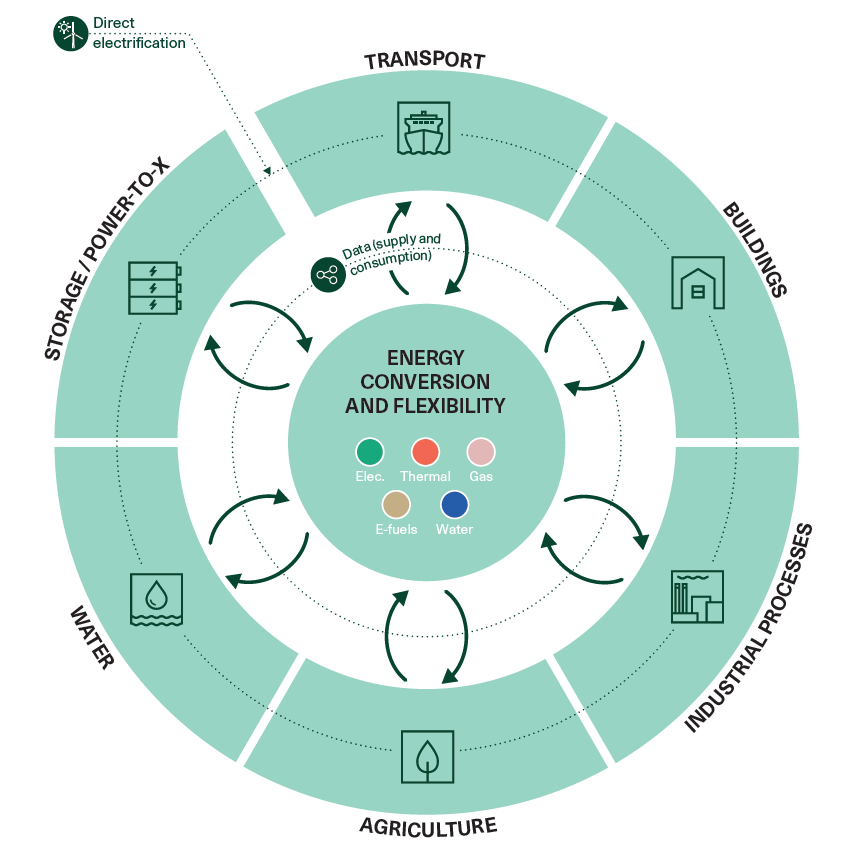
As the shift towards renewable energy picks up pace, the focus on how to build a much more integrated energy system that allows for renewable energy to be efficiently utilised by flowing between energy sectors has intensified accordingly. Essentially, energy production and energy consumption need to be tied together in a much tighter and more intelligent way. The entire energy system must be interconnected in innovative ways, breaking down traditional boundaries between heating, cooling, water, gas, e-fuels and electrical power in the planning and development of the future green energy system.
Fostering new ways of collaboration
Sector coupling involves dismantling traditional silos between different forms of energy, and fostering partnerships and collaborations across sectors and industries both locally, nationally and internationally. In Denmark, there is a long-standing tradition of close collaboration between the public and private sector, and between players of different industries. That collaboration is founded on developing mutually beneficial solutions to a common challenge through knowledge sharing and partnerships.
About the white paper “Sector coupling – Unlocking renewable energy’s full potential”
This white paper presents highlights on sector coupling in a Danish context with a focus on energy. Coupling sectors establish new streams for renewable energy to displace fossil fuels on the path toward carbon neutrality. Using concrete examples of application, it presents an overview of how Denmark works to utilise renewable energy in sectors such as heating, cooling, transport, production industries and farming, while at the same time securing a high degree of energy efficiency and security of supply.