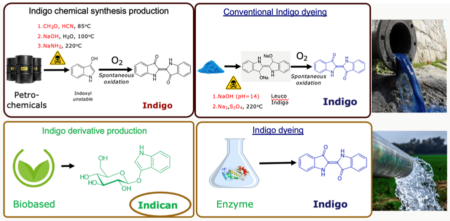
Solution provider

The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability (DTU-Biosustain) at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) aims to develop new knowledge and technologies to support the transformation from conventional, and often unsustainable, industrial production methods to a sustainable bio-based industry. Our research contributes to developing sustainable products within 3 categories – Microbial Food, Sustainable Chemicals, and Natural Products - using microbial production hosts called cell factories.